Channels and Attribution in Google Analytics 4
It is very helpful to familiarize yourself with common terminology for ad traffic and attribution for understanding advertising reports in Google Analytics 4. This article is a mini guide to clarify the terminology for understanding Ad reports in Google Analytics 4.
When visitors land on your website, they are coming from some source. e.g. when a user searches on Google and click on search result to open the website, their source is an organic Google search. If a user opens a website directly, source will be Direct. This leads us to the very first level of categorization of Ad traffic.
Source/Medium
The Source/Medium classification allows us to categorize traffic. “Medium” refers to the category of traffic, while “Source” represents the actual origin of the traffic. Here are some examples:
| Medium | Source |
|---|---|
| CPC (Cost Per Click ads) | Google/CPC |
| CPC (Cost Per Click ads) | Bing/CPC |
| Display ads | Facebook/Display |
| Referral | googleanalytics4.co/referral |
Channels
Channels in Google Analytics 4 group together related Source/Medium combinations. They provide a broader view of traffic sources. In Universal Analytics, these groupings were customizable. In GA4, as of this writing date. It is not customizable. For the sake of understanding, lets consider a very simple rule below
| Channel ( Example only) | Source/Medium Included |
|---|---|
| Paid Search | Google/CPC OR Bing/CPC |
| Social Media | Facebook/Organic OR Twitter/Organic |
| Email Marketing | Newsletter/Email |
| Direct | (Direct) |
In the above example , looking at first row any traffic which has either Google/CPC or Bing/CPC will be classified as Paid Search channel.
Since GA4 no longer allows for customized definition of Channels. It is more important than ever to understand the rules of Channel definition and tag your campaigns accordingly.
Channels for Manual traffic tagging
Manual traffic tagging means you are using utm_source and utm_medium parameters in your referral links. E.g. In this link, I have added two parameters utm_source=AdArtcile and utm_medium=explanation. Google Analytics will read the values of utm_source and utm_medium and then apply the set of rules given below to determine which channel this traffic would be classified as. (for this example, the channel would be unassigned, as it does not meet any rule )
| Channel | Source Criteria | Criteria Combination | Medium Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | Source exactly matches “(direct)” | AND | Medium is one of -(not set), -(none) |
| Cross-network | Campaign Name contains “cross-network” | AND | Cross-network includes Discovery, Performance Max, and Smart Shopping |
| Paid Shopping | Source matches a list of shopping sites | OR | Campaign Name matches the regex ^(.*(([^a-df-z] |
| Paid Search | Source matches a list of search sites | AND | Medium matches the regex ^(.cp.|ppc|retargeting|paid.*)$ |
| Paid Social | Source matches a regex list of social sites | AND | Medium matches the regex ^(.cp.|ppc|retargeting|paid.*)$ |
| Paid Video | Source matches a list of video sites | AND | Medium matches the regex ^(.cp.|ppc|retargeting|paid.*)$ |
| Display | – | – | Medium is one of (“display”, “banner”, “expandable”, “interstitial”, “cpm”) |
| Paid Other | – | AND | Medium matches the regex ^(.cp.|ppc|retargeting|paid.*)$ |
| Organic Shopping | Source matches a list of shopping sites | OR | Campaign name matches the regex ^(.*(([^a-df-z] |
| Organic Social | Source matches a regex list of social sites | OR | Medium is one of “social”, “social-network”, “social-media”, “sm”, “social network”, “social media” |
| Organic Video | Source matches a list of video sites | OR | Medium matches the regex ^(.video.)$ |
| Organic Search | Source matches a list of search sites | OR | Medium exactly matches “organic” |
| Referral | – | – | Medium is one of “referral”, “app”, or “link” |
| Source matches “email”, “e-mail”, “e_mail”, or “e mail” | OR | Medium matches “email”, “e-mail”, “e_mail”, “e mail” | |
| Affiliates | – | – | Medium matches “affiliate” |
| Audio | – | – | Medium exactly matches “audio” |
| SMS | Source exactly matches “sms” | OR | Medium exactly matches “sms” |
| Mobile Push Notifications | – | OR | Medium ends with “push” |
| Medium contains “mobile” or “notification” | |||
| Source exactly matches “firebase” | |||
| unassigned | No channel rules meet. |
Channels for Google Ads traffic
Channels for Google ads traffic are defined with a combination of source platform and Google ads campaign type. In GA4 report you see the channel as Paid shopping, it would mean its source platform is Google Ads and the campaign type for the campaign is shopping.
| Channel | Source Platform | Google Ads Campaign Type |
|---|---|---|
| Paid Shopping | Google Ads | Shopping |
| Paid Search | Google Ads | Google Search or Google Partners |
| Paid Video | Google Ads | YouTube Search or YouTube Videos |
| Display | Google Ads | Google Display Network |
| Cross-network | Google Ads | Cross-network, including -Discovery, -Performance Max, -Smart Shopping. |
| Paid Social | Google Ads | Social |
Channels for Non-Google Ads traffic (SA360)
Since SA360 supports both Google Ads and other Ad platforms ( e.g. Bing ). Its channel categorization for Google Ads platform is same as above. For non-Google Ads platforms, it has additional rules which are
| Channel | Source Platform | Search Ads 360 Engine Account Type |
|---|---|---|
| Paid Search | SA360 | bing, yahoo gemini, yahoo.jp, baidu, admarketplace, naver, 360.cn, yandex |
| Paid Social | SA360 | facebook, twitter |
Channels for Merchant Center traffic
Merchant center traffic has only one rule.
| Channel | Source Platform |
|---|---|
| Organic Shopping | Shopping Free Listings |
Sequence & Path
A sequence is the order in which a user may visit your website. E.g. First visit can be from Google search engine without clicking an Ad. Second visit can be from Google search after clicking an Ad.
The path describes the sequence of channels through which a user arrives and interacts with your website. Here are some path examples:
- Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Conversion
- Direct -> Email Marketing -> Conversion
- Social Media -> Referral -> Conversion
Attribution
Attribution is a decision to allocate credit/weightage to different channels in the path to conversion.
E.g.
First, click attribution
Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Conversion ( First click attribution would give all credit to : organic search )
Last click attribution
Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Conversion ( last click attribution: would give all credit to Paid search)
Attribution Model Types in GA4
Different attribution models assign credit or weightage to channels in varying ways. Default attribution model for reports in GA4 is Data-driven model. The attribution model which GA4 supports are given below. GA4 will be sunsetting
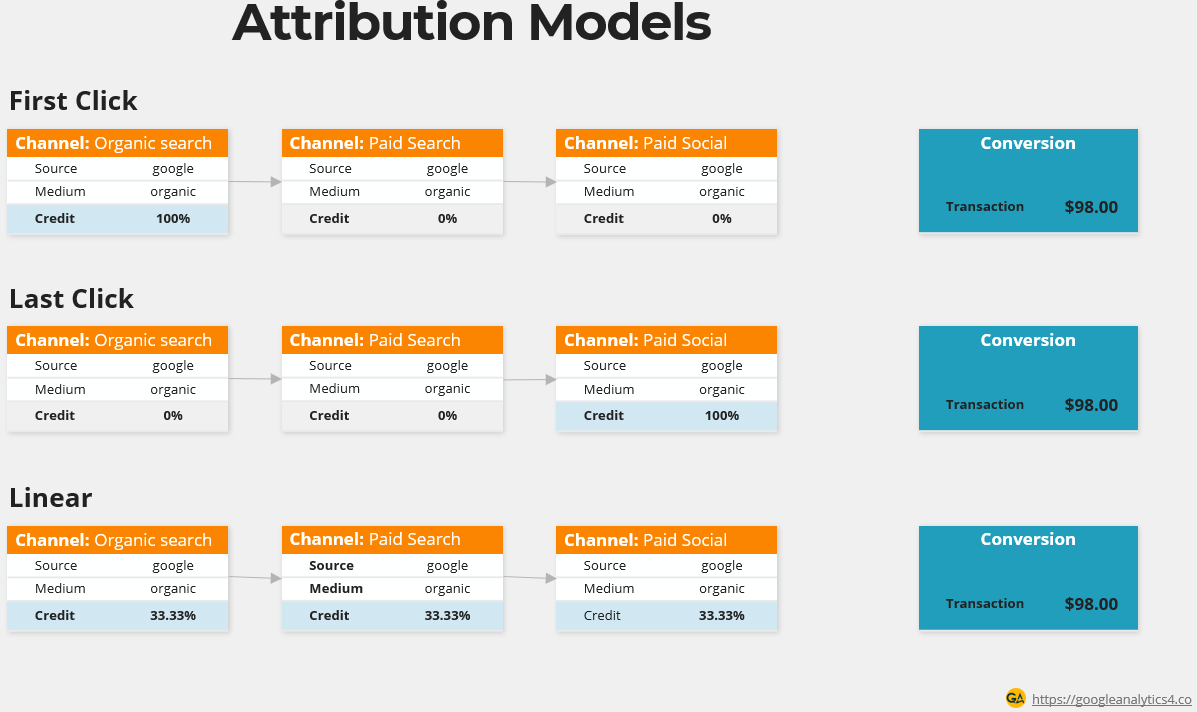
First Click Attribution
First Click Attribution gives credit for a conversion or sale to the first touchpoint or interaction a user had with a marketing channel. This attribution model will be removed from GA4 in late 2023.
| Path | Attribution |
|---|---|
| Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Paid Social ->Conversion | Organic Search: 100% Paid Search: 0% Paid Social: 0% |
The first touchpoint is Organic Search in this example. Since its first click attribution, all the credit goes to first touchpoint. The subsequent touchpoints (Paid Search and Paid Social) receive no credit.
Cross-channel Last Click Attribution
Last Click Attribution assigns all the credit for a conversion or sale to the final touchpoint or interaction that occurred before the conversion.
| Path | Attribution |
|---|---|
| Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Paid Social ->Conversion | Organic Search: 0% Paid Search: 0% Paid Social: 100% Conversion |
In the Last Click Attribution model, all the credit is attributed to the last touchpoint, which is Paid Social in this example. The previous touchpoints Organic Search and Paid Search receive no credit.
Google paid channels Last Click Attribution
Attributes 100% of the conversion value to the last Google Ads channel that the customer clicked through before converting. If there is no Google Ads click in the path, it falls back to Paid and organic last click. Looking at the same example from Google Ad Last click attribution model. It will drop the credit given to Paid Social, rather it will give 100% of the credit to Paid Search.
| Path | Attribution |
|---|---|
| Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Paid Social ->Conversion | Organic Search: 0% Paid Search: 100% Paid Social: 0% Conversion |
Linear Attribution:
In the linear attribution model, credit is evenly distributed among all channels in the conversion path. This attribution model will be removed from GA4 in late 2023. Here’s an example in tabular form:
| Path | Attribution |
|---|---|
| Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Paid Social -> Conversion | Organic Search: 33.33% Paid Search: 33.33% Paid Social: 33.33% Conversion |
Position-Based Attribution:
The position-based attribution model gives more weight to the first and last channels in the conversion path, while the remaining channels share the rest.This attribution model will be removed from GA4 in late 2023. Here’s an example:
| Path | Attribution |
|---|---|
| Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Paid Social -> Conversion | Organic Search: 40% Paid Search: 10% Paid Social: 40% Conversion |
Time Decay Attribution
In the time decay attribution model, channels closer to the conversion receive more credit, while channels earlier in the path receive less. This attribution model will be removed from GA4 in late 2023. Here’s an example:
| Path | Attribution |
|---|---|
| Organic Search -> Paid Search -> Paid Social -> Conversion | Organic Search: 10% Paid Search: 30% Paid Social: 60% Conversion |
Data-Drive Attributions
Data-driven attribution uses Artificial Intelligence to understand the impact each touchpoint has on conversion. Its the default algorithm for GA4 reports. The details of the algorithm are a black box for the end user. For now, we cannot tweak the parameters or understand what “data-driven” mean other than a generic label that it is AI-driven attribution.
Wrapping up:
By categorizing incoming traffic through source/medium classification and grouping related combinations into channels, marketers and analysts can gain a broader view of their traffic sources. Since GA4 no longer allows customizable channel definitions, it is crucial to understand the predefined channel rules and properly tag campaigns for accurate attribution.
The sequence and path of user interactions on a website provide ground for attribution models. These models help allocate credit to different channels along the conversion path. Whether it’s first-click attribution, last-click attribution, linear attribution, or data-driven attribution, each model offers unique perspectives on channel effectiveness and can go a long way in improving return on investment on marketing spend.

Responses