Understanding Consent Mode in Google Analytics 4
Google introduced consent mode with Google Analytics 4. It adds an additional layer of control for data collection (privacy protection) for Google Analytics and Google Ads.
Google Analytics uses cookies to gather and store information about user behavior. A cookie is a small file stored on a web browser where the website is being loaded. It stores information such as a unique identifier to identify the user or preference whether the user wants to see an Ad or not. With consent mode, you can control the cookie behavior. Prior to consent mode, if you had Google Analytics installed on your website, you did not have control over what data could be written on cookies.
Consent Types
Google Analytics provides the following consent options.
| Consent Type | Description |
| ad_storage | Enables storage (such as cookies) related to advertising. |
| analytics_storage | Enables storage (such as cookies) related to analytics e.g. visit duration. |
| functionality_storage | Enables storage that supports the functionality of the website or app e.g. language settings. |
| personalization_storage | Enables storage related to personalization e.g. video recommendations |
| security_storage | Enables storage related to security such as authentication functionality, fraud prevention, and other user protection. |
We can make it simpler with an actual example.
Consent Mode Example with Google Analytics 4
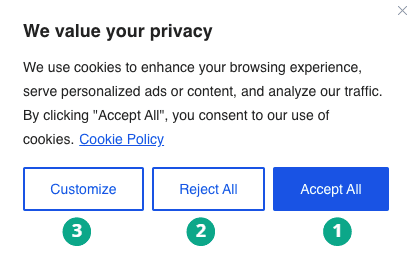
Consider a scenario where Google Analytics is installed on a website. When a user visits the website following pop-up is shown giving user 3 choices.
- Accept All
- Reject All
- Customize

We will now look into what these choices can mean and how we will use Google Analytics’ consent mode to modify data collection.
1. Accept All
Clicking this option means the user accepts this website’s cookie policy. Assuming our cookie policy allows for default data collection of Google Analytics. Our Google Analytics tag can now do the following :
- Read or write first-party analytics cookies
- Store numeric identifiers to model user behavior.
- Store personalization information to show ads.
- Store any other information for all consent types.
The configuration for Accept All at the backend will be
| Consent Type | Parameter value |
| ad_storage | granted |
| analytics_storage | granted |
| functionality_storage | granted |
| personalization_storage | granted |
| security_storage | granted |
2. Reject All
Clicking this option means user rejects the website’s cookie policy. “Consent mode” can now set parameters to inform the analytics collection tag.
- Do not read or write first-party analytics cookies.
- Do not allow for ad personalization cookies.
- Do not store any kind of information.
Cookieless Data in Reject All
When cookies are not allowed, google will send cookieless pings to the server. This enables google to model user behavior from anonymous pings. Following cookieless data is sent to the server.
- Cookieless signals for consent state: Actual state whether the user has Accepted / Rejected the privacy policy.
- Cookieless conversion pings: Anonymous data when a conversion occurs.
- Cookieless google analytics ping: A ping is sent from all pages where Google Analytics beacon is loaded and when events are triggered.
The configuration for Reject All at the backend will be:
| Consent Type | Parameter value |
| ad_storage | denied |
| analytics_storage | denied |
| functionality_storage | denied |
| personalization_storage | denied |
| security_storage | denied |
3. Customize
Certain websites allow users to customize their cookie preferences. As an example, let us say the user chose to customize and refused the website permission to store any ads data or personalization data while allowing other types of data.
The configuration for this scenario at the backend will be :
| Consent Type | Parameter value |
| ad_storage | denied |
| analytics_storage | granted |
| functionality_storage | granted |
| personalization_storage | denied |
| security_storage | granted |
Privacy Options:
Consent mode settings can be configured with code logic based on end-users’ choice (accept/reject etc). Google Analytics 4 and Google Ads also provide privacy options. These options can be configured from Google Analytics and Google Ads interfaces.
| Privacy Option | Function | Analytics Parameter |
| allow_google_signals | When disabled, events sent from the tag will not be used for ads personalization, demographics, and interests reports. | No effect when not set or set to true. When set to false, all join beacons are suppressed. |
| allow_ad_personalization_signals | when disabled, events will not be used for ad personalization, but signals can be used for demographics and interests reporting. | No effect when not set or set to true. When set to false, include an &npa=1 parameter on all beacons. |
| restricted_data_processing | When enabled, Google will limit how it uses the events sent from the tag. It will not use events data for A. Adding users to remarketing lists, B. Adding users to similar audience remarketing seed lists, and related functionality. |
No effect when not set. When set to true, an &rdp=1 parameter is included in beacons. When set to false, an &rdp=0 parameter is included in beacons. |
Configuring Consent Settings:
Consent settings are configured via Google Tag Manager. Privacy parameters on the other hand can be turned on or off from the actual interface of Google Analytics or Google Ads. You can follow this guide to learn how to configure consent mode settings in Google Analytics 4 with Google Tag Manager.

Responses